Analysis of Successful Application Cases of Small-Scale Fire Detection Systems in Urban Firefighting
In recent years, with the continuous maturation of IoT, artificial intelligence, and image recognition technologies, the role of small-scale fire detection systems in fire early warning and emergency response has become increasingly prominent. These systems typically rely on high-precision sensors, infrared thermal imaging, and drone patrols to achieve real-time monitoring and early warning of fire incidents, providing technical support for urban firefighting and forest fire prevention. Through precise localization and rapid response, the system can pinpoint the source of a fire in its initial stages, effectively reducing the risk of fire spread and safeguarding people's lives and property.

I. Urban Firefighting Scenarios
Application Background
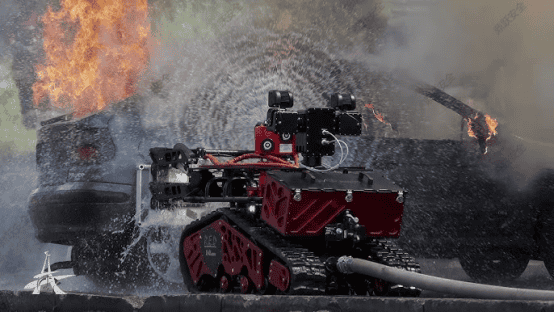
Urban fires often present challenges such as complex building structures, rapid fire spread, and high risks of trapped occupants. Traditional manual reconnaissance suffers from information delays and significant safety hazards. Through lightweight design, high mobility, and real-time communication capabilities, the compact fire reconnaissance system has become the "intelligent vanguard" of urban firefighting.
Case Analysis
In high-rise building fires, firefighters struggle to quickly pinpoint the source of the fire and the distribution of trapped individuals. Compact fire reconnaissance systems equipped with thermal imaging cameras and gas sensors can penetrate deep into the fire scene to scan, transmitting real-time data on fire source temperatures, toxic gas concentrations, and the locations of trapped individuals. For instance, during a fire at an urban complex, the system rapidly pinpointed the ignition point via infrared thermal imaging and detected areas with excessive CO concentrations within the building, providing critical data for rescue route planning and minimizing casualties.
The system supports real-time video transmission and two-way voice communication, enabling the command center to remotely guide on-site rescue operations via live footage. During a chemical plant fire, the system used its remote voice broadcast feature to direct trapped workers to safety zones while simultaneously streaming live footage from the fire scene to command center monitors, aiding in the development of precise firefighting strategies.
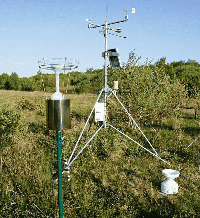
II. Forest Fire Prevention Scenarios
Application Context
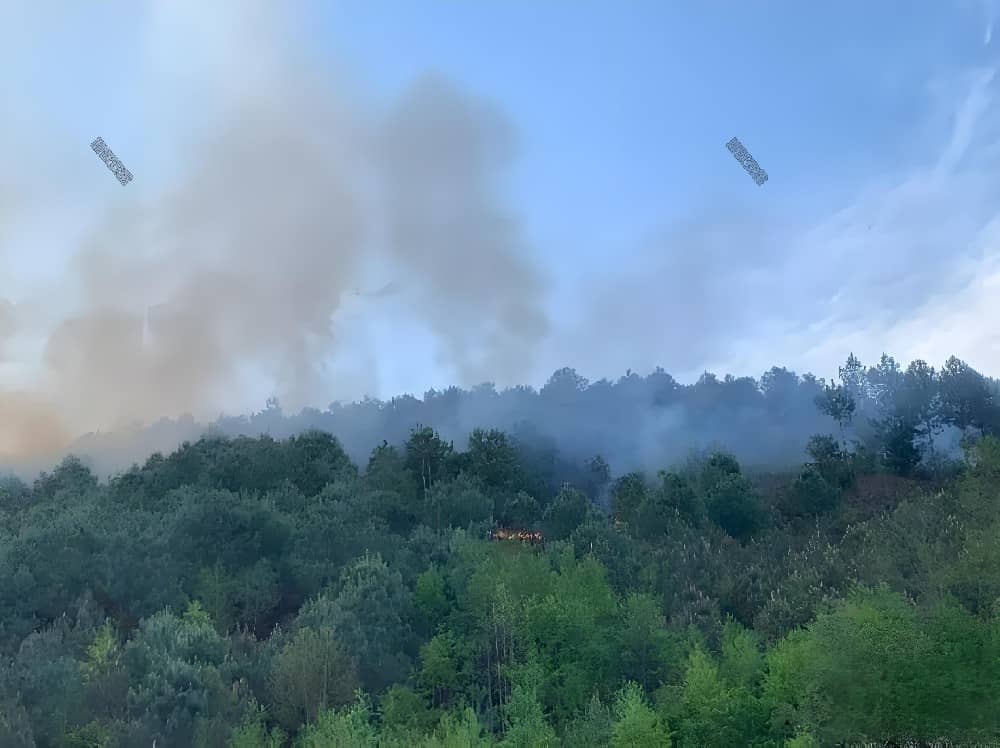
Forest fire prevention and control face challenges such as vast geographical areas and difficult patrols. Traditional patrol methods are relatively inefficient, whereas small-scale fire detection systems leverage remote monitoring, drone inspections, and satellite communication technologies to achieve large-scale, low-cost, and round-the-clock fire monitoring.
Case Analysis
At a national forest park, real-time monitoring of key forest areas is achieved through a combined approach of fixed-position small fire detection equipment and drone patrols. Fixed devices handle routine monitoring, while drones conduct scheduled patrols and capture imagery of hotspots during high-risk periods, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
The system integrates meteorological data such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed with image data for comprehensive analysis. Through a big data platform, it enables fire trend prediction and regional risk assessment. When monitoring data triggers an alert, the system automatically uploads fire information to the command center while simultaneously notifying nearby patrol teams and firefighting forces via satellite or wireless networks, facilitating rapid response and on-site handling.

III. Conclusion: A New Paradigm for Fire Prevention Empowered by Technology
Through technological innovation and scenario adaptation, the small-scale fire detection system has demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in both urban and forest fire prevention. Its core value lies in:
Risk Proactive Management:Shifting from reactive firefighting to proactive prevention, reducing fire occurrence rates through predictive modeling.
Precision Rescue:Data-driven decision-making reduces resource waste and secondary harm.
Ecological Sustainability:Protecting forest resources and urban safety, supporting the achievement of the "dual carbon" goals.
As technology continues to evolve, such systems will become core tools for building smart cities and ecological security barriers, driving the evolution of emergency response systems toward greater efficiency and safety.