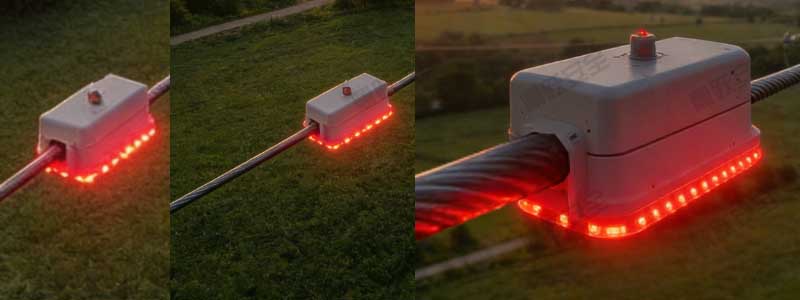
Crane Proximity Warning System for Electrical Emergencies
I. Background and Significance
In high-voltage transmission lines, substations, and other live-line work zones, large construction machinery such as cranes faces the risk of inadvertently entering safety protection zones during operations. This can trigger arc flashes, electric shock incidents, or equipment damage. To ensure the safety of personnel and equipment while enhancing emergency response capabilities in the power sector, the implementation of proximity warning devices for real-time monitoring and early warning of cranes is of paramount importance.

II. Technical Principles and Operational Mechanisms
Detection Principle:Proximity warning devices typically operate based on non-contact voltage detection technology. By sensing changes in high-voltage electric fields, they continuously monitor the distance between cranes and energized equipment or transmission lines. When the sensing antenna detects an electric field strength exceeding a preset critical threshold, it indicates the crane has approached a hazardous zone.
Early Warning Mechanism:The system incorporates a built-in safety distance threshold. When the actual measured distance falls below the safety value, the system triggers an alarm, prompting personnel to evacuate or halt operations promptly, thereby preventing electric shock incidents and other electrical safety accidents.

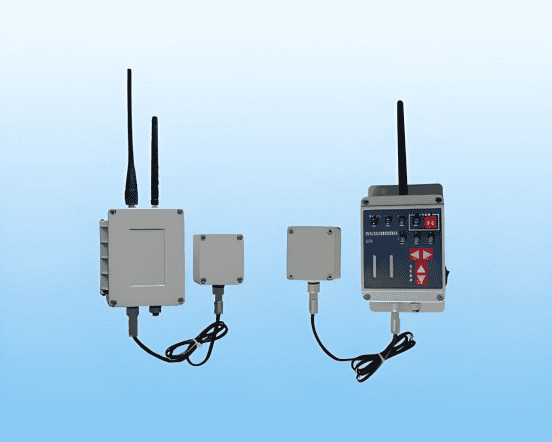
III. System Architecture and Equipment Configuration
The proposal recommends integrating crane proximity warning devices into the power emergency management system, with the main components including:
Sensing Detection Module:Utilizes high-sensitivity non-contact electric field sensors to collect real-time electric field data around the crane.
Data Processing and Control Module: Built-in microcontroller or embedded processing system processes acquired electric field data, compares it against safety thresholds, and determines whether to trigger an alarm.
Early Warning Display and Alarm Module:Includes audible and visual alarm devices (such as buzzers,LED indicators) and a digital display for intuitive status indication; can transmit early warning information to the central control room via the remote communication module.
Communication Module:Utilizing wireless communication (such asLTE or Wi-Fi), it transmits early warning information in real time to power dispatch centers or emergency command centers, enabling remote monitoring and joint dispatch.
Human-Machine Interaction Module: Through operation of buttons, touchscreens, and other methods, it allows operators to acknowledge, reset, or take emergency measures in response to warnings.
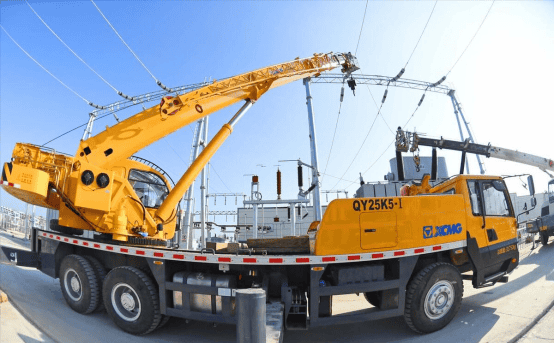
IV. Implementation Steps for the Emergency Response Plan
Preliminary Planning and Risk Assessment:Conduct a risk assessment of electrical facilities within the crane operation zone to determine safety distances and electric field threshold values for different areas. Develop an installation plan for early warning devices and equipment layout diagrams to ensure coverage of all critical risk points.
Equipment Installation and Commissioning: Install proximity warning sensors and associated data processing units in crane and high-voltage work zones. Conduct initial commissioning, calibrate warning thresholds through finite element simulation and field measurements, ensuring a safety margin of at least 20% or higher when alarms are triggered.
System Integration and Coordination: Integrate the crane proximity warning system with the power dispatch center and emergency response platform to enable real-time transmission and processing of warning information. Develop control strategies for automatic shutdown, emergency power disconnection, or other interlocked protective measures.
Emergency Drills and Personnel Training: Regularly conduct on-site drills for the early warning system, simulating scenarios where cranes enter hazardous zones. These exercises test alarm response and emergency procedures, while training operators and dispatchers to ensure they are familiar with warning signals and corresponding response protocols.
Operational Management and Post-Operation Inspection:Establish a routine inspection and periodic maintenance mechanism for equipment to ensure critical components such as sensors and communication modules remain in optimal working condition. Continuously optimize system parameters and early warning models based on operational data and incident alert feedback.
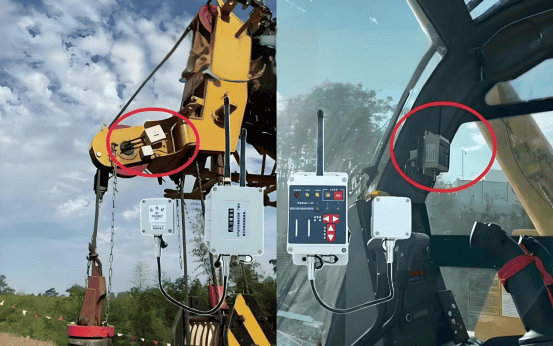
V. Safety Assurance and Expected Outcomes
Real-time Monitoring and Dynamic Early Warning: By continuously monitoring electric field strength, the system can issue immediate alerts when cranes approach energized areas, ensuring personnel can promptly take evasive actions.
Data Logging and Incident Tracking:The system automatically records early warning data, providing technical support and data evidence for incident root cause analysis, equipment upgrades and retrofits, and subsequent contingency plan refinement.
Enhanced Safety Margin:Field testing demonstrates that the actual safety distance during alarms exceeds standard values by0.7 to 1.6 meters, ensuring greater redundancy in early warnings and significantly reducing accident risks caused by operator errors or sensor inaccuracies.

VI. Conclusion
By integrating crane proximity warning systems into power emergency response plans, real-time monitoring of distances between cranes and high-voltage live facilities is enabled. This system also rapidly issues warning signals during abnormal situations, providing multi-layered protection for personnel, equipment, and the power grid. Implementing this solution helps reduce safety accident risks caused by proximity to high-voltage live areas during construction, further safeguarding the secure and stable operation of power systems while providing technical support for power emergency management.